Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Chapter 9 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the Class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Coordination Compounds Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Coordination number of Ni in [Ni(C2O4)3]4– is
(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer
B
Question. CrCl3 has primary valence of
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d) 1
Answer
A
Question. O2 is a
(a) Monodentate ligand
(b) Bidenate ligand
(c) Tridentate ligand
(d) Hexadenate ligand
Answer
B
Question. When AgNO3 is added to a solution of Co(NH3)5Cl3, the precipitate of AgCl shows two ionisable chloride ions. This means :
(a) Two chlorine atoms satisfy primary valency and one secondary valency
(b) One chlorine atom satisfies primary as well as secondary valency
(c) Three chlorine atoms satisfy primary valency
(d) Three chlorine atoms satisfy secondary valency
Answer
A
Question. As per IUPAC nomenclature, the name of the complex [Co(H2O)4(NH3)2]Cl3 is :
(a) Tetraaquadiaminecobalt (III) chloride
(b) Tetraaquadiamminecobalt (III) chloride
(c) Diaminetetraaquacoblat (II) chloride
(d) Diamminetetraaquacobalt (III) chloride
Answer
D
Question. The number of ions formed on dissolving one molecule of FeSO4(NH4)2SO4.6H2O in water is:
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 3
(d) 6
Answer
B
Question. An ambident ligand is one which
(a) is linked to the metal atom through two donor atoms
(b) has two donor atoms, but only one of them has the capacity to form a coordinate bond [or a sigma (σ) bond]
(c) has two donor atoms, but either of two can form a coordinate bond
(d) forms chelate rings.
Answer
C
Question. The solution of K4[Fe(CN)6] in water will
(a) give a test K+
(b) give a test Fe2+
(c) give a test of CN–
(d) give a test of [Fe(CN)6]4–
Answer
A
Question. Chemical formula for iron (III) hexacyanoferrate (II) is
(a) Fe[Fe(CN)6]
(b) Fe3[Fe(CN)6]
(c) Fe3[Fe(CN)6]4
(d) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
Answer
D
Question. The coordination number of a central metal atom in a complex is determined by
(a) the number of ligands around a metal ion bonded by sigma and pi-bonds both
(b) the number of ligands around a metal ion bonded by pi-bonds
(c) the number of ligands around a metal ion bonded by sigma bonds
(d) the number of only anionic ligands bonded to the metal ion.
Answer
C
Question. As per IUPAC nomenclature, the name of the complex [Co(H2O)4(NH3)2]Cl3 is :
(a) Tetraaquadiaminecobalt (III) chloride
(b) Tetraaquadiamminecobalt (III) chloride
(c) Diaminetetraaquacobalt (II) chloride
(d) Diamminetetraaquacobalt (III) chloride
Answer
D
Question. In Ni(CO)4– , oxidation number of Ni is :
(a) 4
(b) – 4
(c) 0
(d) + 2
Answer
C
Question. Which ligand is expected to be bidentate?
(a) C2O42-
(b) CH3C ≡ N
(c) Br –
(d) CH3NH2
Answer
A
Question. [EDTA]4- is a :
(a) monodentate ligand
(b) bidentate ligand
(c) quadridentate ligand
(d) hexadentate ligand
Answer
D
Question. The hypothetical complex chlorodiaquatriamminecobalt (III) chloride can be represented as
(a) [CoCl(NH3)3(H2O)2]Cl2
(b) [Co(NH3)3(H2O)Cl3]
(c) [Co(NH2)3(H2O)2 Cl]
(d) [Co(NH3)3(H2O)3]Cl3
Answer
A
Question. The coordination number and the oxidation state of the element ‘E’ in the complex [E (en)2 (C2O4)]NO2 (where (en) is ethylene diamine) are,respectively,
(a) 6 and 2
(b) 4 and 2
(c) 4 and 3
(d) 6 and 3
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following complexes are heteroleptic ?
(i) [Cr(NH3 )6 ]3+ (ii) [Fe(NH3)4Cl2 ]+
(iii) [Mn(CN)6 ]4- (iv) [Co(NH3)4Cl2 ]
(a) (i), (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Some salts although containing two different metallic elements give test for only one of them in solution. Such salts are
(a) complex
(b) double salts
(c) normal salts
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. K4[Fe(CN)6 ] is a :
(a) double salt
(b) complex compound
(c) acid
(d) base
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is NOT a ligand ?
(a) PH3
(b) NO+
(c) Na+
(d) F–
Answer
C
Question. The ligand N(CH2CH2NH2)3 is
(a) tridentate
(b) pentadentate
(c) tetradentate
(d) bidentate
Answer
C
Question. An example of ambidentate ligand is
(a) Ammine
(b) Aquo
(c) Chloro
(d) Thiocyanato
Answer
D
Question. The IUPAC name for the complex [Co(ONO)(NH3)5]Cl2 is
(a) pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(II) chloride
(b) pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(III) chloride
(c) nitrito-N-pentaamminecobalt(III) chloride
(d) nitrito-N-pentaamminecobalt(II) chloride
Answer
B
Question. A bidenate ligand always
(a) has bonds formed to two metals ions
(b) has a charge of +2 or – 2
(c) forms complex ions with a charge of +2 or –2
(d) has two donor atoms forming simultaneously two sigma (σ) bonds.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following species is not expected to be a ligand?
(a) NO
(b) NH4+
(c) NH2CH2CH2NH2
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Question. According to Lewis, the ligands are
(a) acidic in nature
(b) basic in nature
(c) some are acidic and others are basic
(d) neither acidic nor basic
Answer
B
Question. NH2-NH2 serves as
(a) Monodentate ligand
(b) Chelating ligand
(c) Bridging ligand
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
C
Question. The IUPAC name of K2[PtCl6] is
(a) hexachloroplatinate potassium
(b) potassium hexachloroplatinate (IV)
(c) potassium hexachloroplatinate
(d) potassium hexachloroplatinum (IV)
Answer
B
Question. Glycinato ligand is:
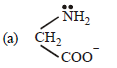
(b) bidentate ligant
(c) two donor sites N and O–
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Which one does not belong to ligand?
(a) PH3
(b) NO+
(c) BF3
(d) Cl–
Answer
C
Question. Which one is the most likely structure of CrCl3. 6H2O if 1/3 of total chlorine of the compound is precipitated by adding AgNO3
(a) CrCl3. 6H2O
(b) [ Cr (H2O)3 Cl3]. (H2O)3
(c) [ CrCl2 (H2O)4 ] Cl . 2H2O
(d) [ CrCl (H2O)5 ] Cl2 . H2O
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following postulates of Werner’s theory is incorrect?
(a) Primary valencies are satisfied by negative ions.
(b) Secondary valencies are satisfied by neutral molecules or negative ions.
(c) Secondary valence is equal to the coordination number and it depends upon the nature of ligand attached to metal.
(d) The ions/ groups bound by the secondary linkages to the metal have charecteristic spatial arrangements.
Answer
C
Question. The stabilisation of cooordination compounds due to chelation is called the chelate effect. Which of the following is the most stable complex species ?
(a) [Fe(CO)5 ]
(b) [Fe(CN)6 ]3 –
(c) [Fe(C2O4 )3 ]3 –
(d) [Fe(H2O)6 ]3+
Answer
C
Question. A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent ?
(a) thiosulphato
(b) oxalato
(c) glycinato
(d) ethane – 1, 2-diamine
Answer
A
Question. The compound having the lowest oxidation state of iron is:
(a) K4Fe(CN)6
(b) K2FeO4
(c) Fe2O3
(d) Fe(CO)5
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following complexes are homoleptic ?
(i) [Co(NH3 )6 ]3+ (ii) [Co(NH3 )4Cl]+
(iii) [Ni(CN)4 ] 2- (iv) [Ni(NH3 )4Cl2 ]
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
C
Question. The oxidation state of Cr in [Cr(NH3 )4Cl2 ]+ is
(a) 0
(b) + 1
(c) + 2
(d) + 3
Answer
D
Question. Ligand in a complex salt are
(a) anions linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal atom or ion
(b) cations linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal or ion
(c) molecules linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal or ion
(d) ions or molecules linked by coordinate bonds to a central atom or ion
Answer
C
Question.Central atoms/ions in coordination compounds are.
(a) Lewis acid
(b) Lewis bases
(c) Neutral molecules
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. One mole of the complex compound Co(NH3)5Cl3, gives 3 moles of ions on dissolution in water. One mole of the same complex reacts with two moles of AgNO3 solution to yield two moles of AgCl (s). The structure of the complex is
(a) [Co(NH3)3Cl3]. 2 NH3
(b) [Co(NH3)4Cl2] Cl . NH3
(c) [Co(NH3)4Cl] Cl2. NH3
(d) [Co(NH3)5Cl] Cl2
Answer
D
Question. K3[Al(C2O4 )3] is called
(a) Potassium aluminooxalate
(b) Potassium trioxalatoaluminate (III)
(c) Potassium aluminium (III) oxalate
(d) Potassium trioxalatoaluminate (VI)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following does not form a chelate ?
(a) EDTA
(b) Oxalate
(c) Pyridine
(d) Ethylenediamine
Answer
C
Question. The IUPAC name of the coordination compound K3[Fe(CN)6 ] is
(a) Tripotassium hexacyanoiron (II)
(b) Potassium hexacyanoiron (II)
(c) Potassium hexacyanoferrate (III)
(d) Potassium hexacyanoferrate (II)
Answer
C
Question. In the coordination compound, K4[Ni(CN)4], the oxidation state of nickel is
(a) 0
(b) +1
(c) +2
(d) –1
Answer
A
Question. The IUPAC name of [Ni(NH3)4] [NiCl4] is
(a) Tetrachloronickel (II) – tetraamminenickel (II)
(b) Tetraamminenickel (II) – tetrachloronickel (II)
(c) Tetraamminenickel (II) – tetrachloronickelate (II)
(d) Tetrachloronickel (II) – tetrachloronickelate (0)
Answer
C
Question. According to the postulates of Werner for coordination compounds
(a) primary valency is ionizable
(b) secondary valency is ionizable
(c) primary and secondary valencies are non-ionizable
(d) only primary valency is non-ionizable.
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following ligands forms a chelate
(a) Acetate
(b) Oxalate
(c) Ammonia
(d) Cyanide
Answer
B
Question.The IUPAC name of the complex [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl]Cl2 is
(a) aquatetramminechloridocobalt (III) chloride
(b) chloridoaquatetramminechloridocobalt (III) chloride
(c) chloridoaquatetramminechloridocobalt (III) chloride
(d) tetrammineaquachloridocobalt (III) chloride
Answer
D
Question. What is the denticity of the ligand ethylenediaminetetra actetate ion?
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 6
(d) 1
Answer
C

