Students should refer to Worksheets Class 11 Chemistry The p-Block Elements Chapter 11 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 11 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 11 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 11 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
The p-Block Elements Worksheets Class 11 Chemistry
Question. Red phosphorus is chemically less reactive because
(a) It does not contain P – P bonds
(b) It dos not contain tetrahedral P4 molecules
(c) It does not catch fire in air even upto 400°C
(d) It has a polymeric structure
Answer
D
Question. Fertilizer having the highest nitrogen percentage is:
(a) Calcium cyanamide
(b) Urea
(c) Ammonium nitrate
(d) Ammonium sulphate
Answer
B
Question. Nitrogen (I) oxide is produced by:
(a) Thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrate
(b) Disproportionation of N2O4
(c) Thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrite
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. On heating boron with caustic potash, the pair of products formed are
(a) Potassium Borate + Dihydrogen
(b) Potassium Borate + Water
(c) Potassium Borate + H2
(d) Borax + Dihydrogen.
Answer
A
Question. In the compound of type ECl3, where E = B, P, As, or Bi, the angle Cl – E – Cl for different E are ion the order:
(a) B = P = As = Bi
(b) B > P > As > Bi
(c) B < P = As = Bi
(d) B < P < As < Bi
Answer
B
Question. Which phosphorus is used as a rat poison?
(a) White
(b) Violet
(c) Red
(d) Black
Answer
A
Question. In white phosphorous(P4) molecule, which one is not correct:
(a) 6P-P single bonds are present
(b) 4P-P single bonds are present
(c) 4 lone pair of electrons is present
(d) P-P-P bond angle is 60°
Answer
A
Question. In general, the Boron Trihaides act as
(a) Strong reducing agent
(b) Lewis Acids
(c) Lewis Bases
(d) Dehydrating Agents
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following will not produce hydrogen gas ?
(a) Reaction between Fe and dil. HCl
(b) Reaction between Zn and NaOH
(c) Reaction between Zn and conc. H2SO4
(d) Electrolysis of NaCl in Nelsons cell
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements regarding ozone is not correct?
(a) The oxygen-oxygen bond length in ozone is identical with that of molecular oxygen
(b) The ozone is response hybrid of two structures
(c) The ozone molecule is angular in shape
(d) Ozone is used as a germicide and disinfectant for the purification of air.
Answer
A
Question. Carbon-60 contains
(a) 20 pentagons and 12 hexagons
(b) 12 pentagons and 20 hexagons
(c) 30 pentagons and 30 hexagons
(d) 24 pentagons and 36 hexagons.
Answer
B
Question. The element with smallest atomic radius and lowest melting point out of the following is
(a) Al
(b) Ga
(c) In
(d) Tl
Answer
B
Question. Fluorine is more electronegative than either boron or phosphorus. What conclusion can be drawn from the fact that BF3 has no dipole moment but PF3 does?
(a) BF3 is not spherically symmetrical, but PF3 is.
(b) BF3 molecule must be linear.
(c) The atomic radius of P is larger than the atomic radius of B.
(d) The BF3 molecule must be planar triangular.
Answer
D
Question. Al and Ga have nearly the same covalent radii because of
(a) greater shielding effect of s-electrons of Ga atom
(b) poor shielding effect of s-electrons of Ga atom
(c) poor shielding effect of d-electrons of Ga atom
(d) greater shielding effect of d-electrons of Ga atom.
Answer
C
Question. The stability of +1 oxidation state among Al, Ga, In and Tl increases in the sequence
(a) Al < Ga < In < Tl
(b) Tl < In < Ga < Al
(c) In < Tl < Ga < Al
(d) Ga < In < Al < Tl
Answer
A
Question. Aluminium is more reactive than iron but aluminium is less easily corroded than iron because
(a) aluminium is a noble metal
(b) iron undergoes reaction easily with water
(c) aluminium with oxygen forms a protective oxide layer
(d) iron forms mono and divalent ions.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following structures correctly represents the boron trifluoride molecule?
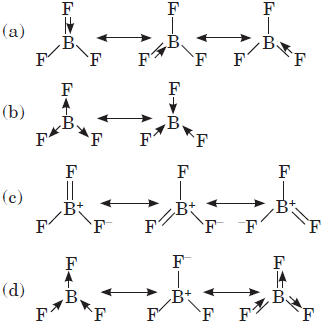
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following conceivable structures for CCl4 will have a zero dipole moment?
(a) Square planar
(b) Square pyramid (carbon at apex)
(c) Irregular tetrahedron
(d) Regular tetrahedron
Answer
D
Question. In the carbon family, the elements other than carbon do not form pπ-pπ bonds because the atomic orbitals are too
(a) small and diffused to undergo effective lateral overlap
(b) large and diffused to undergo effective lateral overlap
(c) large and far, too less diffused to overlap linearly
(d) small to overlap both laterally and linearly.
Answer
B
Question. Aluminium vessels should not be washed with materials containing washing soda since
(a) washing soda is expensive
(b) washing soda is easily decomposed
(c) washing soda reacts with Al to form insoluble aluminium oxide
(d) washing soda reacts with Al to form insoluble aluminate.
Answer
D
Question. What is the hybridisation of B in BCl3?
(a) sp3
(b) sp2
(c) sp
(d) dsp2
Answer
B
Question. Which is least stable compound?
(a) BCl3
(b) GaCl3
(c) InCl3
(d) TlCl3
Answer
D
Question. Boron is unable to form BF63– because of
(a) high electronegativity of boron
(b) high electronegativity of fluorine
(c) lack of d-orbitals in boron
(d) less difference in electronegativity between B and F.
Answer
C
Case Based MCQs :
The heavier members of 13 and 14 groups besides the group oxidation state also show another oxidation state which is two units less than the group oxidation state. Down the group (↓), the stability of higher oxidation state decreases and that of lower oxidation state increases. This concept which is commonly called inert pair effect has been used to explain many physical and chemical properties of the element of these groups.
Question. The strongest reductant among the following is
(a) SnCl2
(b) SnCl4
(c) PbCl2
(d) GeCl2
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement is wrong?
(a) Tl(III) salt undergo disproportionation.
(b) CO is used as a reducing agent.
(c) CO2 is a greenhouse gas.
(d) SiO2 is a covalent solid.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following act as the strongest acid?
(a) Tl2O3
(b) SnO2
(c) PbO2
(d) CO2
Answer
D
Question. Heavier members of groups 13 exhibit oxidation state
(a) +3 only
(b) +1 only
(c) +1 and +3 both
(d) +1, +2, +3
Answer
C
Question. Which among the following is the strongest oxidising agent?
(a) SiO2
(b) GeO2
(c) SnO2
(d) PbO2
Answer
D
Question. Which among the following is the strongest reducing agent?
(a) GaCl
(b) InCl
(c) BCl3
(d) TlCl
Answer
C
Allotropy : The phenomenon of existence of the same substance (element or compound) in two or more forms, in the same physical state, having different properties. Different forms are called allotropes or allotropic modifications.
Except lead, all other elements of group 14 show allotropy.

Question. The element that does not show catenation among the following p-block elements is
(a) carbon
(b) silicon
(c) germanium
(d) lead.
Answer
D
Question. Fullerene with formula C60 has a structure where every carbon atom is
(a) sp-hybridized
(b) sp2-hybridized
(c) sp3-hybridized
(d) not hybridized.
Answer
B
Question. Wood charcoal is used in gas masks because it
(a) is poisonous
(b) liquefies gases
(c) is porous
(d) adsorbs poisonous gases.
Answer
D
Question. Thermodynamically the most stable form of carbon is
(a) diamond
(b) graphite
(c) fullerene
(d) coal.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not sp2 hybridised?
(a) Graphite
(b) Graphene
(c) Fullerene
(d) Dry ice
Answer
D
The high charge and small size of Al3+ ion gives it a high charge density which is responsible for its tendency to show
(a) covalency in its compounds in the gaseous state
(b) high hydration enthalpy which stabilizes its compounds in solution, and
(c) high lattice enthalpy of its compounds in the solid state.
Hence, aluminium can form both covalent and ionic bond. Like halides of boron, halides of aluminium do not show backbonding because of increase in size of aluminium. In fact, aluminium atoms complete their octets by forming dimers. Thus, chloride and bromide of aluminium exist as dimers. Thus, chloride and bromide of aluminium exist as dimers, both in the vapor state and in polar solvents like benzene, while the corresponding boron halides exist as monomer. In boron trihalides, the extent of back bonding decreases with increase in size of halogens and thus Lewis acid character increases. All BX3 are hydrolysed by water but BF3 shows as different behavior.
Question. The dimeric structure of aluminium chloride disappear when
(a) it dissolves in water
(b) it reacts with donor molecules like R3N
(c) it dissolves in benzene
(d) both (a) and (b).
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) All boron trihalides form back bonding.
(b) Anhydrous aluminium chloride is an ionic compound.
(c) Aluminium bromide make up the electron deficiency by bridging with other aluminium bromide.
(d) None of these.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following reaction is incorrect?
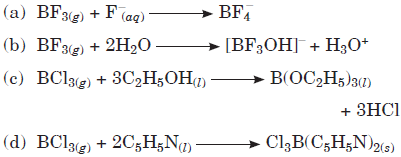
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements about anhydrous aluminium chloride is correct?
(a) It exists as Al2Cl6 dimer in vapour form.
(b) It is not easily hydrolysed.
(c) It sublimes at 100°C under vacuum.
(d) It is a strong Lewis base.
Answer
A

