Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 6 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Biology based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Biology for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance Worksheets Class 12
Question. The two strands of DNA are held together by
(a) peptide bonds
(b) phosphodiester bonds
(c) hydrogen bonds
(d) S – S bonds
Answer
C
Question. Chargaff’s rules are applicable to
(a) single stranded RNA.
(b) single stranded DNA and RNA.
(c) single stranded DNA.
(d) double stranded DNA.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is correct for Watson and Crick’s model of DNA. It is duplex with
(a) 10 base pairs and 3.4 Å distance for every turn.
(b) 10 base pairs and 3.4 Å distance for each turn of spiral.
(c) 20 base pairs and 34 Å for each turn.
(d) None of the above
Answer A
A
Question. Nucleosome is
(a) intron interrupted DNA.
(b) double helix DNA.
(c) negatively charged DNA wrapped around positively charged histone octomer.
(d) satellite DNA.
Answer
C
Question. Histones are rich in
(a) alanine and glycine
(b) lysine and arginine
(c) histidine and serine
(d) cysteine and tyrosine
Answer
B
Question. In Streptococcus pneumoniae
(a) virulent form is smooth.
(b) virulent form is rough.
(c) nonvirulent form is capsulated.
(d) all forms are rough.
Answer
A
Question. During infection of E. coli cells by bacteriophage T2,
(a) proteins are the only phage components that actually enter the infected cell.
(b) both proteins and nucleic acids enter the cell.
(c) only proteins from the infecting phage can also be detected in progeny phage.
(d) only nucleic acids enter the cell.
Answer
D
Question. In some viruses, RNA is present instead of DNA indicating that
(a) their nucleic acid must combine with host DNA before replication.
(b) they cannot replicate.
(c) there is no hereditary information.
(d) RNA can act to transfer heredity.
Answer
D
Question. Leading strand during DNA replication is formed
(a) continuously.
(b) in short segments.
(c) first.
(d) ahead of replication.
Answer
A
Question. Methyl guanosine triphosphate is added at 5′ end of hn-RNA in a process of
(a) tailing
(b) splicing
(c) capping
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Segments of mRNA removed during splicing are called ______.
(a) introns
(b) exons
(c) promotor regions
(d) integrator regions
Answer
A
Question. Initiation codon of protein synthesis (in eukaryotes) is
(a) GUA
(b) GCA
(c) CCA
(d) AUG
Answer
D
Question. Lactose operon produces enzymes
(a) b-galactosidase, permease and glycogen synthetase.
(b) b-galactosidase, permease and transacetylase.
(c) permease, glycogen synthetase and transacetylase.
(d) b-galactosidase, permease and phosphoglucose isomerase.
Answer
B
Question. Who proved that DNA is basic genetic material?
(a) Griffith
(b) Watson
(c) Boveri and Sutton
(d) Hershey and Chase
Answer
D
Question. Satellite DNA
(a) is classified in many categories such as microsatellites, minisatellites, etc. on the basis of base composition length of segments and number of repetitive units.
(b) normally does not code for any protein.
(c) shows polymorphism.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Polymorphism in DNA sequence
(a) is the basis of genetic mapping of human genome.
(b) arises due to mutation.
(c) is the basis of DNA finger printing.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. SNP which is pronounced as “snips” stands for
(a) Small Nuclear Protein
(b) Single Nucleotide Particle
(c) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
(d) Small Nicking Points
Answer
C
Statement Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question. Which of the following statement is correct about DNA polymerase ?
(a) DNA polymerase can synthesize mRNA in the 3′ to 5′ direction.
(b) DNA polymerase can synthesize DNA in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
(c) DNA polymerase can synthesize mRNA in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
(d) DNA polymerase can synthesize DNA in the 3′ to 5′ direction.
Answer
B
Question. Select the correct statement regarding protein synthesis.
(a) When the small subunit of the ribosome encounters an mRNA the process of translation begins.
(b) Peptidase catalyses the formation of peptide bond.
(c) UTRs are present between the start codon and stop codon.
(d) At the end of translation, the release factor binds to the initiation codon.
Answer
A
Question. Identify the incorrect statement about RNA.
(a) RNA was the first genetic material to evolve in the living systems.
(b) Apart from being a genetic material, it is also a catalyst.
(c) DNA evolved from RNA with chemical modifications.
(d) RNA being a catalyst is non-reactive and stable.
Answer
D
Question. Choose the incorrect statement regarding the observations drawn from the human genome project.
(a) Repetitive sequences are stretches of RNA.
(b) Less than 2 per cent of the genome codes for protein.
(c) SNPs help in tracing human history.
(d) Repetitive sequences make up a very large portion of the human genome.
Answer
A
Question. Select the two correct statements out of the four (i–iv) given below about lac operon.
(i) Glucose or galactose may bind with the repressor and inactivate it.
(ii) In the absence of lactose, the repressor binds with the operator region.
(iii) The z-gene codes for permease.
(iv) This was elucidated by Francois Jacob and Jacque Monod.
(a) (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) r-RNA provides the template for synthesis of proteins.
(ii) t-RNA brings amino acids and reads the genetic code.
(iii) RNA polymerase binds to promoter and initiates transcription.
(iv) A segment of DNA coding for polypeptide is called intron.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer
D
Question. Select the incorrect statement(s).
(i) Six codons do not code for any amino acid.
(ii) Codon is read in mRNA in a contiguous fashion.
(iii) Three codons function as stop codons.
(iv) The initiation codon AUG codes for methionine.
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer
A
Assertion / Reason Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : Adenine cannot pair with cytosine
Reason : Adenine and cytosine do not have a perfect match between hydrogen donor and hydrogen acceptor sites. Hence, they cannot pair.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The genetic code is degenerate.
Reason : Most amino acids are coded by more than one codon.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : DNA fingerprinting is very well known for its application in paternity testing is case of disputes.
Reason : It employs the principle of polymorphism in DNA sequences as the polymorphisms are inheritable from parent to children.
Answer
B
Matching Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question. Match the following and choose the correct combination from the given options.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Splicing | I. Lac operon |
| B. Okazaki fragments | II. Lagging strands |
| C. Jacob and Monad | III. Lactose |
| D. Inducer | IV. Removal of intron |
(a) A – IV; B – II; C – I; D – III
(b) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – III; C – I; D – II
(d) A – II; B – III; C – I; D – IV
Answer
A
Question. Match the steps of protein by synthesis given in column-I with their feature given in column-II and select the correct combination from the given options.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Termination | I. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase |
| B. Translation | II. Okazaki fragments |
| C. Transcription | III. GTP dependent release factor |
| D. DNA replication | IV. RNA polymerase |
(a) A – II; B – I; C – III; D – IV
(b) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(c) A – IV; B – III; C – I; D – II
(d) A – II; B – III; C – I; D – IV
Answer
B
Question. Match the codons given column I with their respective amino acids given in column II and choose the correct answer.
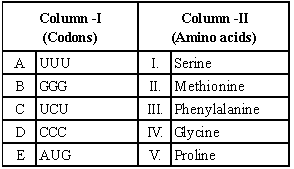
(a) A – III; B – IV; C – I; D – V; E – II
(b) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – V; E – II
(c) A – III; B – IV; C – V; D – I; E – II
(d) A – II; B – IV; C – I; D – V; E – III
Answer
A
Question. Match the scientists given in column-I with their work given in column-II and select the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. F. Meischer | I. DNA double helix |
| B. Griffith | II. Nuclein |
| C. Hershey and | III. S. pneumoniae Chase |
| D. Watson and Crick | IV. Bacteriophages |
| E. Wilkins and | V. X-ray diffraction studies Franklin |
(a) A – II; B – III; C –IV; D – I; E – V
(b) A – V; B – IV; C –III; D – I; E – II
(c) A – I; B – III; C –IV; D – II; E – V
(d) A – I; B – IV; C –III; D – II; E – V
Answer
A
Question. Match column-I (Scientists) with column-II (Discoveries) and select the correct options.
| Column-I (Scientists) | Column-II (Discoveries) |
| A. Alec Jeffreys | I. Lac operon |
| B. F. Sanger | II. Automated DNA sequences |
| C. Jacob and Monod | III. DNA finger printing |
| D. Avery, Mc Leod | IV. Transforming principle and McCarty |
(a) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
(b) A – III; B – II; C – I; D – IV
(c) A – III; B – II; C – IV; D – I
(d) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV
Answer
B
Diagram Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question. Name the types of synthesis A and B occurring in the replication fork of DNA as shown below.

(a) A – Continuous synthesis (synthesis of leading strand); B – Discontinuous synthesis (synthesis of lagging strand).
(b) A – Discontinuous synthesis (synthesis of leading strand); B – Continuous synthesis (synthesis of lagging strand).
(c) A- Continuous synthesis (synthesis of lagging strand); B – Discontinuous synthesis (synthesis of leading strand).
(d) A – Discontinuous synthesis (synthesis of lagging strand); B – Continuous synthesis (synthesis of leading strand).
Answer
A
Question. The diagram given below shows an important concept (proposed by C) in the genetic implication of DNA. The process occuring in that concept are marked as A and B.
Identify A, B and C.
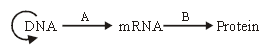
(a) A-Translation, B – Transcription, C-Erwin Chargaff
(b) A-Transcription, B – Translation, C-Francis Crick
(c) A-Translation, B – Extension, C-Rosalind Franklin
(d) A-Transcription, B – Replication, C-James Watson
Answer
B
Question. Given figure represent the DNA double helix model, proposed by Watson and Crick (1953). Select the option that shows correct measurement of A, B and C marked in the figure.
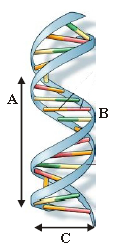
(a) A – 3.4 nm, B – 0.34 nm, C – 2 nm
(b) A – 34 nm, B – 3.4 nm, C – 20 nm
(c) A – 3.4 Å, B – 0.34 Å, C – 20 Å
(d) A – 34 Å, B – 3.4 Å, C – 2 Å
Answer
A
Question. The given figure shows lac operon model and its functioning. Select the option which correctly labels A, B, X, Y and Z marked in the figure and also identify the label (L) which is primarily responsible for the hydrolysis of the disaccharide, lactose, into galactose & glucose.
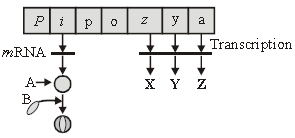
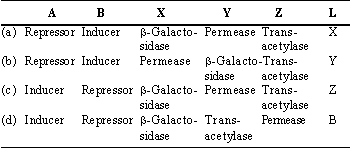
Answer
A
Question. Identify the labels A, B, C and D in the given structure of tRNA and select the correct option.

(a) Anticodon TyC loop AA binding DHU loop site
(b) AA binding TyC loop Anticodon DHU loop site loop
(c) AA binding DHU loop Anticodon TyC loop site loop
(d) AA binding DHU loop TyC loop Anticodon site loop loop
Answer
B
Critical Thinking Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question. RNA polymerases used for the transcription of genes require a ______ template.
(a) rRNA
(b) DNA
(c) RNA
(d) mRNA
Answer
B
Question. In terms of DNA and RNA structure, what is a nucleotide ?
(a) A nucleotide is a heterocyclic base.
(b) A nucleotide is a sugar molecule covalently bonded to a heterocyclic base.
(c) A nucleotide is a sugar molecule bonded to phosphate group and a heterocyclic base.
(d) A nucleotide is a heterocyclic base bonded to phosphate group.
Answer
C
Question. Escherichia coli fully labelled with 15N is allowed to grow in 14N medium. The two strands of DNA molecule of the first generation bacteria have
(a) different density and do not resemble with their parent DNA.
(b) different density but resemble with their parent DNA.
(c) same density and resemble with their parent DNA.
(d) same density but do not resemble with their parent DNA.
Answer
A
Question. During elongation of polypeptide chain, sigma factor is
(a) functionless.
(b) retained for specific function.
(c) released for re-use.
(d) required during closing of chain.
Answer
A
Question. Operon is a
(a) sequence of three nitrogen bases determining a single amino acid.
(b) set of closely placed genes regulating a metabolic pathway in prokaryotes.
(c) segment of DNA specifying a polypeptide.
(d) gene responsible for switching on and switching off other genes.
Answer
B
Question. DNA replication is semi-conservative as
(a) only non-parent strand acts as template.
(b) both strands of new molecule are synthesized de novo.
(c) one of the strand in each new molecule is parental and the other is new.
(d) daughter strands are dispersive.
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following pair is a purine pair?
(a) Uracil, Guanine
(b) Cytosine, Thymine
(c) Adenine, Guanine
(d) Adenine, Thymine
Answer
C
Question. The two strands of a double helix model of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between
(a) sugar and phosphate groups.
(b) sugar and nitrogenous bases.
(c) phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases.
(d) nitrogenous bases.
Answer
D
Question. Consider the process that a cell uses to replicate its doublestrand DNA to make copies for daughter cells. Which statement describes the DNA in daughter cells ?
(a) The double helix in one daughter cell consists of two strands that were originally in the parent cell, while the double helix in the other daughter cell consists of two newly made strands.
(b) The two strands of the double helices in both daughter cells consist of segments of new and parental DNA.
(c) The double helices in each daughter cell consists of one parental strand and one newly made strand.
(d) None of the above.
Answer
C
Question. A geneticist isolates a gene for a specific traits under study, she also isolate the corresponding mRNA. Upon comparison, the mRNA is found to contain 1,000 fewer bases than the DNA sequence. Did the geneticist isolate the wrong DNA ?
(a) Yes, mRNA is made from a DNA template and should be the same length as the gene sequence.
(b) Yes, the mRNA should contain more bases than the DNA sequence because bases flanking the gene are also transcribed.
(c) No, the final mRNA contains only exons, the introns were removed.
(d) No, the mRNA was partially degraded after it was transcribed.
Answer
C
Question. During translation, proteins are synthesized by
(a) ribosomes using the information on DNA.
(b) lysosome using the information on DNA.
(c) ribosome using the information on mRNA.
(d) lysosome using the information on mRNA.
Answer
C
Question. What is the main function of tRNA in relation to protein synthesis ?
(a) Initiates transcription
(b) Inhibits protein synthesis.
(c) Identifies amino acids and transport them to ribosomes.
(d) proof reading.
Answer
C
Question. What sequence on the template strand of DNA corresponds to the first amino acid inserted into a protein ?
(a) TAC
(b) UAC
(c) UAG
(d) AUG
Answer
A
Question. What effect would you expect if gene expression of the lac operon were completely repressed ?
(a) The cell would be more efficient without ‘wasting’ the energy required for the low level of Lac Z, LacY, and Lac A gene expression.
(b) Allolactose would accumulate within the cell and become toxic.
(c) Lactose would not be converted into the inducer and the operon could not be induced.
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. In addition to the human genome sequence, draft or finished genome sequences existed for eight model organisms by 2002. Which of the following organisms are not the part of that group of eight model organisms ?
(a) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
(b) Drosophila melanogaster
(c) Oryza sativa
(d) Quercus rubra
Answer
D
Question. DNA fingerprinting using Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs) is based on the observation that
(a) every individual has unique alleles at each VNTR locus.
(b) the DNA of VNTR loci is more stable than that of loci which code for proteins.
(c) VNTR sequences show little variability.
(d) VNTR loci are highly polymorphic.
Answer
D
