Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Biology Organisms and Populations Chapter 13 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Biology based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Biology for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Organisms and Populations Worksheets Class 12 Biology
Question. The famous ‘Australian havoc’ is associated with which of the following invasive species :-
(a) Nile pearch
(b) Princkly pear cactus
(c) Red fox
(d) Rabbit
Answer
B
Question. In rocky intertidal communities removal of which of the following predator became the cause of destruction of 10 species of invertebrates?
(a) Monarch butterfly
(b) Starfish pisater
(c) Paramecium aurelia
(d) Abingdon tortoise
Answer
B
Question. Behavioural response to cope with variations in the environment can be seen in
(a) CAM plants
(b) Opuntia plant
(c) Desert lizards
(d) C4 – plants
Answer
C
Question. Find out the correct match with reference to their habitat –
(a) Mango tree – Canada
(b) Snow leopards – Kerela forest
(c) Tuna fish – Temperate latitudes in oceans
(d) Lion – Gujarat
Answer
D
Question. Temperature is one of the important abiotic factor.Significance of temperature on living beings can be realised through –
(a) Kinetics of enzymes
(b) Basal metabolism
(c) Physiological functions
(d) All the above
Answer
D
Question. Population ecology is an important area of ecology because it links ecology with
(a) Population genetics
(b) Evolution
(c) Physiognomy
(d) Both 1 and 2
Answer
D
Question. The tiger counting in our national parks and tiger reserves is often based on
(a) Pug marks
(b) Manual counting
(c) Fecal pellets
(d) Both 1 and 3
Answer
D
Question. Match the following
| (a) Breeding once in life | (i) Mammals |
| (b) Breeding several times | (ii) Oysters in life |
| (c) Large number of small | (iii) Most of birds sized offsprings |
| (d) Small number of large | (iv) Pacific salmon sized offsprings fish |
(a) a(iv), b(ii), c(iii), d(i)
(b) a(iv), b(iii), c(ii), d(i)
(c) a(iii), b(iv), c(ii), d(i)
(d) a(ii), b(iii), c(iv), d(i)
Answer
B
Question. Match the following given population interactions
(a) + / + (i) Predation
(b) – / – (ii) Ammensalism
(c) + / – (iii) Competition
(c) – / 0 (iv) Mutualism
(a) a(i), b(ii), c(iii), d(iv)
(b) a(i), b(iii), c(ii), d(iv)
(c) a(iv), b(iii), c(i), d(ii)
(d) a(iv), b(iii), c(ii), d(i)
Answer
C
Question. Phytophagous insects show which of the following interaction :-
(a) Predation
(b) Competetion
(c) Mutualism
(d) Commensalism
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following alternative used by zooplanktons to overcome partial stressful conditions ?
(a) Migration
(b) Diapause
(c) Hibernation
(d) Aestivation
Answer
B
Question. Majority of plants belongs to which of the following category
(a) Regulators
(b) Conformers
(c) Partial regulators
(d) Eurytherms
Answer
B
Question. Temperature is the most ecologically relevant environmental factor. In which of the following habitats temperature can exceed 100° C ?
(a) Tropical desert
(b) Thermal springs
(c) Deep sea hydrothermal vents
(d) Both 2 and 3
Answer
D
Question. Next to temperature, water is the most important factor influencing the life of organism. Which among the following water characteristics is not an influencing character?
(a) pH
(b) Turbidity
(c) Colour
(d) Salinity
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following cannot be used by prey for defence against predator :-
(a) Cardiac glycosides
(b) Strychnine
(c) Nectar
(d) Quinine
Answer
C
Question. Regarding competition find out the wrong statement.
(a) Unrelated species could compete for same resource
(b) Fitness of one species is lowered in presence of other species
(c) Abingdon tortoise become extinct due to competitor starfish
(d) Balanus leads to exclusion of Chathamalus from rock coasts of scotland
Answer
C
Statement Type Questions
Question. Consider the following statements (A)-(D) each with one or two blanks.
(A) Bears go into (i) during winter to(ii) cold weather.
(B) A conical age pyramid with a broad base represents(iii) human population.
(C) A wasp pollinating a fig flower is an example of(iv) .
(D) An area with high levels of species richness is known as (v) .Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (i) to (v) in the statements?
(a) (i) – hibernation, (ii) – attract, (iii) – expanding, (iv) – commensalism, (v) – biodiversity park
(b) (i) – hibernation, (ii) – escape, (iii) – expanding, (iv) – mutualism, (v) – hot spot
(c) (i) – aestivation, (ii) – escape, (iii) – stable, (iv) – commensalism, (v) – marsh
(d) (i) – aestivation, (ii) – escape, (iii) – stable, (iv) – mutualism, (v) – hot spot
Answer
B
Question. Study the following statements and answer the question.
(i) Mango trees cannot grow in temperate countries like Canada and Germany.
(ii) Tuna fish are rarely caught beyond tropical latitude in the ocean.
(iii) Snow Leopards are not found in Kerala.
Which of the following factor is responsible for the above statements?
(a) Light
(b) Water
(c) Temperature
(d) Soil
Answer
C
Question. Read the following statements and choose the correct option.
(i) Light is essential for life to exist on the earth.
(ii) Many species of small plants under the canopy to tall trees in forest show optimal use of available light
due to having large sized antenna and higher number of thylakoids.
(iii) UV rays are not harmful to many organisms.
(iv) Photoperiodic requirement is essential for many plants for flowering.
(v) Red algae can live in deeper water of sea because of having pigment, phycoerythrin.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) only (iii)
(d) (i), (ii), (iv) and (v)
Answer
D
Question. Identify the correct statement.
(a) The smaller animals have larger surface area relative to their volume.
(b) Smaller animals are rarely found in polar region.
(c) Bear cannot migrate hence hibernate during winter.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Read the following statements regarding adaptation and choose the correct option.
(i) Many xerophytic plants have a thick cuticle on leaf epidermis and sunken stomata to prevent
transpiration.
(ii) Some xerophytic plants have special photosynthetic pathway (CAM) that enables their stomata to close during day.
(iii) Opuntias has no leaves, they are reduced to spines.
(iv) All adaptation are genetically fixed in all organisms.
(v) In Opuntia, the pathway of photosynthesis is through C3 cycle.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) Only (ii)
(c) (iv) and (v)
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. Mark the incorrect statement.
(a) Many fishes thrive in Antarctic water where temperature is always below zero .
(b) Microbes can survive in hot springs where temperature exceeds 100°C.
(c) Fishes can survive even at a depth where pressure exceeds 100 atm.
(d) Desert lizards have marvelous physiological ability to survive scorching heat of desert.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following are the characteristics of expanding population ?
(i) Pyramid – shaped age structure.
(ii) An urn – shaped age structure.
(iii) Pre-reproductive and reproductive age groups become more or less equal in size.
(iv) Rapidly growing population with high birth rate.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is categorised as a parasite in true sense?
(a) Human foetus developing inside the uterus draws nourishment from the mother.
(b) The female Anopheles bites and sucks blood from humans.
(c) Head louse living on the human scalp as well as laying eggs on human hair.
(d) The cuckoo (koel) lays its eggs in crow’s nest.
Answer
C
Question. Select the incorrect statement.
(a) Overwhelming majority of animals and nearly all plants maintain a constant internal temperature.
(b) An orchid growing as an epiphyte on a mango branch is an example of commensalism.
(c) In brood parasitism, the parasitic bird lays its eggs in the nest of its host and lets the host to incubate
them.
(d) In amensalism, one species is harmed whereas the other is unaffected.
Answer
A
Assertion/Reason Type Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : In a water body, Daphnia populations showed distinct variations in their morphology at different seasons.
Reason : Variations in temperature of water bodies at different seasons influences cyclomorphosis in some organisms.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Species are groups of potentially interbreeding natural populations which are isolated from other such groups.
Reason : Distinctive morphological characters are displayed due to reproductive isolation.
Answer
B
Matching Type Questions
Question. Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct answer.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Pacific Salmon fish | I. Produces a small number of large sized offspring |
| B. Mammals | II. Produces a large number of small sized offspring |
| C. Oysters | III. Breed only once in their lifetime |
| D. Birds | IV. Breed many times during their lifetime |
(a) A – III, B – IV, C – II, D – I
(b) A – I, B – IV, C – II, D – III
(c) A – IV, B – II, C – I, D – III
(d) A – II, B – IV, C – III, D – I
Answer
A
Question. Match Column – I with Column – II and choose the correct option.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Pacific salmon fish | I. Verhulst – pearl logistic growth |
| B. Nt = N0ert | II. Breed only once in life time |
| C. Oyster | III. Exponential growth |
| D. dN/dt = rN[K-N/K] | IV. A large number of small sized offsprings |
(a) A – IV; B – III; C – I; D – II
(b) A – III; B – IV; C – I; D – II
(c) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(d) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
Answer
D
Diagram Type Questions
Question. The given figure shows the diagram match representation of organismic response. Which option gives the correct identification of three types of organisms (marked as A, B & C) in response to abiotic factor?
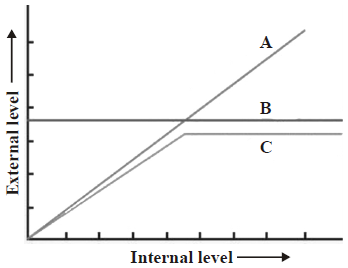
| A | B | C |
| (a) Partial regulator | Regulator | Conformers |
| (b) Regulator | Conformers | Partial regulator |
| (c) Conformers | Regulator | Partial regulator |
| (d) Regulator | Partial regulator | Conformers |
Answer
C
Question. A country with a high rate of population growth took measures to reduce it. The figure below shows age-sex pyramids of populations A and B twenty years apart.
Select the correct interpretation about them.


(a) “B” is earlier pyramid and shows stabilized growth rate.
(b) “B” is more recent showing that population is very young.
(c) “A” is the earlier pyramid and no change has occurred in the growth rate.
(d) “A” is more recent and shows slight reduction in the growth rate.
Answer
D
Question. Identify I to IV which affect the population density.

| I | II | III | IV |
| (a) Increase | Decrease | Increase | Decrease |
| (b) Decrease | Increase | Decrease | Increase |
| (c) Increase | Increase | Decrease | Decrease |
| (d) Decrease | Decrease | Increase | Increase |
Answer
C
Question. In laboratory experiments, two species of the protist Paramecium were grown alone and in the presence of the other species. The following graphs show growth of species 1 (left) and species 2 (right), both along and when in mixed culture.

Interpretation of these graphs shows that
(a) competitive exclusion occurred in these experiments.
(b) both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 1 is less affected.
(c) both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 2 is less affected.
(d) both species are affected equally by interspecific competition.
Answer
C
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. Many freshwater fishes cannot live for long in sea water and vice-versa mainly because of the
(a) variation in light intensity.
(b) change in the levels of thermal tolerance.
(c) osmosis.
(d) spectral quality of solar radiation.
Answer
C
Question. Many animals use the diurnal and seasonal variations in light intensity and photoperiod as cues timing of
(a) for age only
(b) reproductive activities only
(c) migration only
(d) all of these
Answer
D
Question. Regarding temperature and osmotic concentration nearly all plants are
(a) regulator
(b) conformers
(c) partial regulator
(d) escaper in time
Answer
B
Question. The kangaroo rats of North American deserts do not need to drink water because
(a) they meet their water requirement through internal fat oxidation when the water is a byproduct.
(b) they are able to concentrate urine, to minimize water loss.
(c) they do not have sweat glands.
(d) all of the above
Answer
D
Question. Population ecology is an important area of ecology because
(a) it determines the interaction among organisms and between the organisms and its physical environment.
(b) evolutionary changes through natural selection take place at the population level.
(c) it links ecology to population genetics and evolution.
(d) it links different types of communities together.
Answer
C
Question. If in a pond, there were 20 lotus last year and through reproduction 8 new plants are added, taking current population to 28, the birth rate per year is
(a) 0.2
(b) 0.4
(c) 0.6
(d) 0.8
Answer
B
Question. In an age pyramid, the number of individuals of reproductive age is lesser than pre-reproductive but higher than post reproductive ones. The population is
(a) growing
(b) declining
(c) stable
(d) can not be predicted
Answer
A
Question. If N is the population density at time t, then its density at time t + 1 is
(a) Nt + 1 = Nt + [(B + I) + (D + E)]
(b) Nt + 1 = Nt – [(B + I) + (D + E)]
(c) Nt + 1 = Nt + [(B + I) – (D + E)]
(d) Nt + 1 = Nt – [(B + I) – (D + E)]
Answer
C
Question. The integral form of the exponential growth equation is
(a) Nt = N0e–rt
(b) N0 = Ntert
(c) Nt = N0ert
(d) rN = Ntert
Answer
A
Question. Organisms with very high intrinsic growth rates have
(a) long generation times.
(b) short generation times.
(c) no courtship behaviour.
(d) no carrying capacities.
Answer
B
Question. When certain exotic species are introduced into geographical area, they become invasive and start spreading fast because
(a) they have high reproductive rate.
(b) they produce chemicals to inhibit the growth of other organisms.
(c) there is no competition.
(d) the invaded land does not have its natural predators.
Answer
D
Question. Mac Arthur observed that five closely related species of Warblers living on the same tree were able to avoid competition and co-exist due to
(a) cooperation in their foraging efforts.
(b) behavioural differences in their foraging activities.
(c) different kinds of insects they eat.
(d) all of the above
Answer
B
Question. Gause’s ‘competitive exclusion principle’ states that
(a) humans are the most widespread agents of disturbance.
(b) in a competition for similar resource both the participants are benefitted.
(c) in a competition, both the participants are excluded.
(d) two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and
competitively inferior one will be eliminated eventually.
Answer
D

