Please refer to the Globalisation and the Indian Economy Revision Notes given below. These revision notes have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE and KVS books issued for the current academic year. Students will be able to understand the entire chapter in your class 10th Globalisation and the Indian Economy book. We have provided chapter wise Notes for Class 10 Globalisation and the Indian Economy as per the latest examination pattern.
Revision Notes Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Students of Class 10 Globalisation and the Indian Economy will be able to revise the entire chapter and also learn all important concepts based on the topic wise notes given below. Our best teachers for Grade 10 have prepared these to help you get better marks in upcoming examinations. These revision notes cover all important topics given in this chapter.

Globalization refers to the integration of the domestic economy with the economies of the world.
An MNC is a company that owns and controls production in more than one nation.
Foreign Investment is investment made by MNCs.
Liberalization means the removal of barriers and restrictions set by the government on foreign trade.
Governments use trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade to protect the domestic industries from foreign competition. Ex. Tax on imports. Around 1991, government India adopted the policy of liberalization
World Trade Organization (WTO) was started at the initiative of the developed countries. Its main objective is to liberalize international trade.
Privatization means transfer of ownership of property from public sector to private sector.
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) is the contracting of non-primary business activities and functions to a third party service provider.
Multi-lateral Agreement is agreement entered by group of countries.
Mixed economy is a system in which private and public sector work together.
Economic Reforms or New Economic Policy is policy adopted by the Government of India since July 1991. Its key features are Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization (LPG).
Objective Type Questions
Question. What is foreign investment?
(a) Investment made by the foreign governments.
(b) Investment made by the foreign banks.
(c) Investment made by the MNCs.
(d) Investment made by the IMF and World Bank.
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. When and where did the Ford Motors set up their large plant in India?
(a) In 1975 at Pune
(b) In 1985 at Gurugram
(c) In 1995 at Chennai
(d) In 2005 at Mumbai
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. What is the idea behind the development of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in India?
(a) To boost Indian industries.
(b) To solve the problem of unemployment.
(c) To produce handicrafts.
(d) To attract foreign investment.
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
Question.
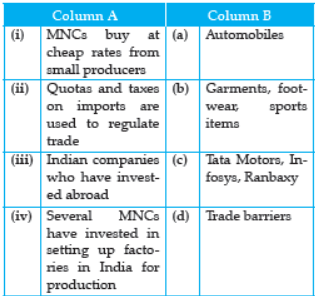
(a) (i)-(a), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(d)
(b) (i)-(b), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(d)
(c) (i)-(b), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(a)
(d) (i)-(a), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(b)
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. Arrange the following in the correct sequence:
(i) Meanwhile, the company’s customer care is carried out through call centres located in India.
(ii) And then has the components manufactured in China.
(iii) A large MNC, producing industrial equipment, designs its products in research centres in the United States.
(iv) These are then shipped to Mexico and Eastern Europe where the products are assembled and the finished products are sold all over the world.
Options:
(a) (iv) – (iii) – (ii) – (i)
(b) (i) – (ii) – (iii) – (iv)
(c) (ii) – (iii) – (i) – (iv)
(d) (iii) – (ii) – (iv) – (i)
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
Question. Find the incorrect option from the following:
(a) MNCs play an important role in the liberalization process.
(b) MNCs control production in more than one country.
(c) MNCs compete with the local producers directly.
(d) MNCs set up their production units close to market.
Answer : Option (a) is incorrect.
Question. Find the incorrect option from the following:
(a) Fair globalisation would create opportunities for all.
(b) MNCs are playing a major role in the globalisation process.
(c) Globalisation has led to improvement in living conditions of all the people.
(d) MNCs have increased their investment in India over the past 20 years.
Answer : Option (c) is incorrect.
Assertion and Reason Based Questions
Question. Assertion (A): The car manufacturing plant of Maruti Udyog Ltd. in India produces cars for Indian markets.
Reason (R): It also exports cars to other developing countries and exports car components for its many factories around the world.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. Assertion (A): Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets.
Reason (R): Foreign trade expands the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
Question. Assertion (A): Local businesses may set up joint production process with MNCs and earn higher profits.
Reason (R): MNCs can provide money for additional investments, like buying new machines for faster production.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
Very Short Answer type Questions
Question. What are SEZ?
Answer : Special Economic Zone
Question. Name the organization lay emphasize Liberalization of foreign trade and Foreign Investment.
Answer : World Trade Organization
Question. What is the most common route for investments by INCs in countries around the world?
Answer : Buy existing local companies
Question. What do you mean by FDI?
Answer : Foreign Direct Investment.
Question. Name two Indian Companies which are also known as MNC.
Answer : TATA Motors, Bajaj;
Question. Why are MNCs setting up their customer care centers in India?
Answer : Due to availability of cheap skilled labour and good English speaking people.
Question. What attracts the foreign investment?
Answer : Infrastructural facilities.
Short Answer type Questions
Question. How does liberalization contribute to the expansion of markets in India?
Answer :
- As a result of liberalization foreign companies are able to set up their offices and markets in India
- The Government of India established many Special Economic Zones where all sorts of facilities made available to foreign companies.
- Foreign companies were allowed flexibility in lab our laws so that they could employ workers for short period.
Question. What are the factors that attract MNCs to set up factories in third world countries?
Answer :
- For better prospectus and profits.
- Favourable government policies
- Availability of highly skilled man power easily and cheaply.
Question. What are the advantages of foreign trade?
Answer :
- Foreign trade gives opportunity to reach buyers in domestic and international markets.
- Choice of the consumers expands manifolds
- The process of similar goods in the markets tends to become equal
Question. What is Tax Barrier? How it helps in regulating the foreign trade?
Answer :
- In some cases it may be necessary to protect local manufacturers from imports.
- Countries set up Tax Barriers to protect their National Interest
- They may be in the form of high import duty and quota restrictions.
Question. What is globalisation?
Answer :
- Integrating a country’s economy with world’s economy
- Foreign producers can sell their goods and services in India and Indian producers can also sell goods and services in other country.
- Inter-dependence of different countries of the world economically
Question. How has technology stimulated the globalization process?
Answer :
- Improvement in transportation technology has made faster delivery of goods across long distances at lower rates.
- Improvement in IT Sector
- Invention of Computers, Internet, Mobile Phones, and Fax etc. has made contacts with people around the world quite easy.
Question. How foreign trade leads to integration of markets?
Answer :
- Trade between countries enables them to extend the boundaries of the market.
- Foreign trade enables countries of the world to consume goods that they are not able to produce
- Foreign trade helps equalizing prices over different parts of the world
Question. “Globalisation has led to the worsening ofthe working conditions of the labourers”. Comment.
Answer :
- Globalisation and open competition leads to insecure working conditions.
- The workers do not get a fair share of profits which the big companies make.
- Workers are exploited by the big companies as they are not given any in- job benefits.
Question. Elaborate any three disadvantages of Multinational Corporations.
Answer : The disadvantages of MNCs are :
(i) Small manufacturers like—batteries, capacitors, plastic toys, tyres, dairy products and vegetable oil are victims of competition.
(ii) Closing down of small units rendered many workers jobless.
(iii) Most employers prefer to employ workers ‘flexibly’, this means that workers jobs are no longer secure.
Small Indian companies are hard hit because of government’s changed policies such as allowing import of the goods which were previously not allowed.
Question. How does foreign trade integrate the markets of different countries? Explain with example.
OR
“Foreign trade integrates the markets in different countries.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : Foreign Trade is integrating markets of different countries:
(i) Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets.
(ii) Producers can sell their products in the markets located in other countries.
(iii) It helps for expanding the choice of goods beyond domestic market.
Question. Describe any three ways in which countries can be linked through globalisation.
Answer : (i) By movement of goods.
(ii) By movement of services.
(iii) By movement of investments.
(iv) By movement of technology.
(v) By the movement of people between countries.
Question. ‘‘Barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment were removed to a large extent in India since 1991.’’ Justify the statement.
Answer : Removal of barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment :
(i) Barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment were partially removed.
(ii) Goods could be imported and exported easily.
(iii) Foreign companies could setup factories and offices here.
(iv) Indian producers got opportunities to compete with producers around the globe.
Question. Explain by giving examples that Multinational Corporations (MNCs) are spreading their production in different ways.
OR
Explain any three ways in which Multinational Companies have spread their production and interaction with local producers in various countries across the globe.
Answer : Multinational Corporations are spreading their production in different ways:
(i) By setting up a partnership with local companies.
(ii) By placing orders with local companies. For example, garments, footwear, sports items, etc.
(iii) By closely competing with the local companies.
Question. “A wide ranging choice of goods are available in the Indian markets.” Support the statement with examples in context of Globalisation.
Answer : A wide ranging choice of good:
(i) We have a wide variety of goods and services before us in the market.
(ii) The latest models of the digital cameras, mobile phones and televisions made by leading manufacturers of the world are available in the market.
(iii) Every season, new models of automobiles can be seen on Indian roads.
(iv) Today Indians are buying cars produced by nearly all the top companies in the world.
Question. How has globalisation affected the life of Indians? Explain with examples.
Answer : Effects of Globalisation:
(i) Advantage to consumers particularly well of sections in the urban areas.
(ii) Wider choice before the consumer.
(iii) Improved quality and lower prices for several products.
Long Answer type Questions
Question. WTOExplain any five positive impacts of globalization.
Answer :
- Globalisation and greater competition among producers have been of advantage to consumers, in terms of wider choice, improved quality and lower prices. Enormous increase in foreign investment through MNCs.
- Several of the top Indian companies have been able to benefit from globalization as they got newer technology and collaboration with foreign companies.
- Some large companies emerged as MNCs Ex. Tata Motors, Infosys.
- New opportunities are created for companies providing services especially those involving IT.
- It has enabled the third world countries to get better technology at a cheaper rate
Question. How do MNCs interlink production across countries?
Answer :
- MNC’s set up their production units in those areas which are quite close to the markets.
- It sets up production jointly with some of the local companies of the selected countries
- Sometimes large MNCs place orders for production with small producers and provide them money for additional investments.
- Sometimes MNCs buy local companies and then expand their production
- Provide latest technology for better and speedy production
Question. What measures can be taken by the government to make globalization fair?
Answer :
- The policies of the government must focus on protecting the interests of all sections of the people.
- Government should ensure that lab our laws are properly implemented and workers get their rights.
- Government should support small industries to face competitions.
- In certain situations, trade and investment barriers should be imposed.
- The government should negotiate at the WTO for fairer rules.
Question. Critically examine the functioning of WTO.
Answer :
- The operations ofthe WTO will lead to undue interference into the internal affairs of different countries.
- Domination of developed countries.
- Serves the interests ofthe developed nations.
- Access to markets of developed countries by developing countries is negligible’
- WTO rules forced the developing countries to remove trade barriers where as many developed countries unfairly retained trade barriers.
Question. What are the factors that have enabled globalisation?
Answer :
- Rapid improvement in technology
- Development in information and communication technology.
- Liberalization of foreign investment policies of the governments.
- Pressure from international organizations
Question. Explain any five negative impacts of globalisation.
Answer :
- Globalisation has led to widening of income inequalities among various countries.
- It has widened the gap between the rich and the poor within the countries.
- It has worsened the working condition of the labourers, especially in the unorganized Sectors.
- The benefits of globalization were not equally distributed among the people, and generally the upper class, in terms of income and education, only got benefited.
- Agricultural sector has been hard hit by the policies of globalization.
Question. What were the main reasons for imposing barriers in Indian after independence?
Answer :
- The term liberalization means the removal of barriers and restrictions set by the government on foreign trade.
- Governments use trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade.
- Trade barriers were used to protect the domestic industries from foreign competition. E.g. Tax on imports.
- It was considered necessary to protect producers within the country from foreign competition.
- The competition from foreign competitors could have crippled the new born industries in India.
Question. Explain any five effects of globalization.
Answer : Five effects of globalization are as follows:
(i) International product launches simultaneously across the entire world.
(ii) Access to international commercial best practices and alignment of local laws with international laws.
(iii) Higher foreign investments in fields like IT, manufacturing and other service sectors and lowering of restrictions on Foreign Direct Investments.
(iv) Increasing Investment in research and development innovative products.
(v) Growth in startups funded by international venture capital firms and angel investors.
Question. How have our markets been transformed in recent years? Explain with examples.
OR
How have our markets been transformed? Explain with examples.
OR
In recent years how our markets have been transformed? Explain with examples.
Answer : Markets have been transformed in recent years:
(i) We have a wide choice of goods and services before us.
(ii) The latest models of digital cameras, mobile phones and televisions made by the leading manufacturers of the world are within our reach now.
(iii) Example: every season new models of automobiles can be seen on Indian roads.
(iv) Today, Indians are buying cars produced by nearly all the top companies in the world.
(v) A similar explosion of brands can be seen for many other goods; from shirts to televisions to processed fruit juices.
Question. Describe the impacts of globalisation on Indian economy with examples.
Answer : Impacts of globalization on Indian economy:
(i) Higher standard of living in urban areas.
(ii) The impact has not been uniform among producers and workers.
(iii) There is the greater choice before the consumers who now enjoy the improved quality and lower prices for several products.
(iv) MNCs have increased their investments in India leading to more job opportunities.
(v) Globalisation has enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as MNCs themselves like Tata Motors, Infosys, Ranbaxy, Asian Paints, etc.
(vi) Globalisation has also created new opportunities for companies providing services particularly those involving IT (Information Technology).
For example, the Indian company producing a magazine for the London based company and call centres.
Question. “Information and Communication technology has played a major role in spreading out production of services across countries.” Justify the statement with examples.
OR
Technology has stimulated the Globalisation process.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer : Rapid improvement in technology has stimulated the globalisation process:
(i) Transportation technology has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
(ii) There are even more remarkable developments in information and communication technology.
(iii) Telecommunication facilities are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas information instantly and to communicate from remote areas.
(iv) Through the internet, one can obtain and share information on almost anything. It also allows sending e-mail and talking across the world at negligible costs.
(v) For example, a news magazine published for London readers is to be designed and printed in Delhi. The text of the magazine is sent through the internet to the Delhi office. The designers in the Delhi office get orders on how to design the magazine from the office in London using telecommunication facilities. The designing is done on a computer. After printing, the magazines are sent by air to London. Even the payment of money for designing and printing from a bank in London to a bank in Delhi is done instantly through the internet.
Question. Describe the role of technology in promoting globalisation process.
Answer : Technology in promoting globalisation process Rapid improvement in technology has stimulated the globalisation process.
(i) This has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
(ii) Even more remarkable have been the developments in information and communication technology.
(iii) Technology in the areas of telecommunications, computers, Internet has been changing rapidly.
(iv) Telecommunication facilities (telegraph, telephone including mobile phones, fax) are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas.
(v) This has been facilitated by satellite communication devices.
Question. How are Multinational Corporations (MNCs) controlling and spreading their productions across the world? Explain.
Answer : The Multinational Corporations (MNCs) are controlling and spreading their production across the world in the following ways:
(i) MNCs setup their production units close to market.
(ii) MNCs setup production units jointly with local companies.
(iii) They setup units where there is skilled and unskilled labour available at low cost.
(iv) Large MNCs in developed countries place orders for production with small producers.
(v) They have tremendous power to determine price, quality, delivery and labour conditions for distant producers.
(vi) By purchasing local companies.
Question. The impact of globalisation has not been uniform.” Demonstrate with the help of illustrations”.
Answer : (i) While globalisation has benefited well off consumers and also producers with skill, education and wealth, many small producers and workers have suffered as a result of the rising competition.
(ii) Removal of trade barriers and liberalisation policies of the governments to facilitate globalisation have hit the local producers and manufactures hard.
(iii) Globalisation and the pressure of competition have substantially changed the lives of workers.
Faced with grow in competition, most employers these days prefer to employ workers ‘flexibly’. This means that workers’ jobs are no longer secure. Illustration : Any one case—either from the text book or beyond it, e.g., MNCs and workers, MNC’s and local manufactures/industries, withdrawal of subsidies, etc.
Case Based Questions
III. Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
Globalization expands and accelerates the movement and exchange of ideas and commodities over vast distances. Globalisation has created more competitive environment in India. In the past two to three decades, more and more MNCs have been looking for locations around the world which would be cheap for their production. Foreign investment by MNCs in these countries has been rising. At the same time, foreign trade between countries has been rising rapidly. A large part of the foreign trade is also controlled by MNCs.
The result of greater foreign investment and greater foreign trade has been greater integration of production and markets across countries. Globalisation is this process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries. MNCs are playing a major role in the globalisation process. More and more goods and services, investments and technology are moving between countries. Besides the movements of goods, services, investments and technology, there is one more way in which the countries can be connected. This is through the movement of people between countries. People usually move from one country to another in search of better income, better jobs or better education.
Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the Globalisation process. Even more remarkable have been the developments in information and communication technology. Globalisation and greater competition among producers – both local and foreign producers – has been of advantage to consumers, particularly the well-off sections in the urban areas. There is greater choice before these consumers who now enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products. As a result, these people today, enjoy much higher standards of living than was possible earlier. Globalisation has also created new opportunities for companies providing services, particularly those involving IT.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
1. Process of integration of different countries is called:
(a) Liberalization
(b) Privatization
(c) Globalization
(d) None of the above
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
2. Globalisation has led to higher standards of living of:
(a) Well-off consumers
(b) Poor consumers
(c) Big producers
(d) None of the above
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
3. Globalisation has created new opportunities of:
(a) Employment
(b) Emerging multinationals
(c) Providing services
(d) All of the above
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
4. Globalisation has posed major challenges for:
(a) Big Producers
(b) Small Producers
(c) Rural Poor
(d) None of these
Answer : Option (b) is correct.



